The Federation of Automobile Dealers Association has released data that shows a dramatic decline in retail vehicle sales. This includes two-wheelers and three-wheelers as well as passenger cars, tractors and commercial vehicles. Sales in September 2024 were down 9.26% from the same period last year. Month-on-month, they showed a decline of 8.88%. This dramatic drop highlights the challenges facing the automotive industry. It may have a negative impact on not only sales, but also economic indicators or consumer confidence in the future.
General Insurance Companies

Analysts and general insurance companies are becoming increasingly worried about the impact that stagnant premiums for third parties and sluggish vehicle sales could have on their financial well-being. As vehicle sales plateau, insurers’ growth opportunities are limited as the number of new policies is reduced. At the same, stagnant premiums for third parties leave little room to adjust revenue. This combination could create a perfect hurricane that puts immense pressure on the loss ratios of FY25 as claims exceed premium income. Insurers could be faced with a difficult financial environment if they don’t take corrective action. Profitability will also become more difficult to maintain.
Decrease in vehicle sales from one year to the next

The Federation of Automobile Dealers Association reported that total retail vehicle sales, including two-wheelers and three-wheelers as well as passenger cars, tractors, commercial vehicles, saw a significant decline of 9.26% from September 2024 to the same time last year. This wasn’t a one-time drop; sales fell 8.88% month-to-month compared to August of 2024. This decline highlights the challenges facing the automotive industry, reflecting both economic headwinds as well as shifting market dynamics. These could have a ripple effect on other industries such insurance and manufacturing.
Continued Decline in August
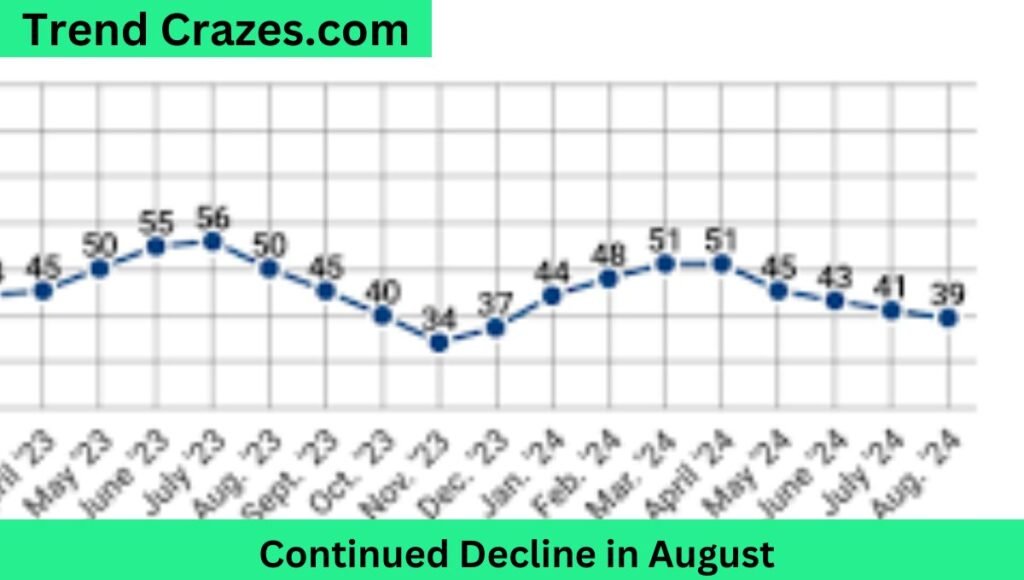
The automotive industry continued to decline in August 2024. It registered a monthly decrease of 7.01% when compared with July 2024. This successive drop indicates deeper market pressures as demand for key vehicle categories is tapering off. The continued slump is raising concerns about the underlying economic condition and consumer sentiment. This further compounds the challenges facing automakers and related industries. As this trend continues, stakeholders closely monitor potential market shifts which could either stabilize the current downturn or worsen it.
Low Sales during the Festive Season

The Federation of Automobile Dealers Association has stated that despite the arrival of the festive season with celebrations such as Ganesh Chaturthi or Onam, auto dealers have seen a lackluster performance. The market has not experienced the festive boom that was expected, but rather a general stagnation. Dealers are struggling with a trend of flat, or even negative growth. This has dampened hopes for seasonal recovery. This lack of demand during traditionally high consumption periods is a concern for the auto industry, and may indicate that consumer spending has been impacted by economic uncertainty.
In April-August of 2024, motor insurance premiums, which include both mandatory third-party and own-damage coverage, increased by 10.3%. This growth is slower than the 18.5% increase recorded during the same time period last year. The slowdown in premium growth could be a reflection of the challenges facing the auto industry. This slower growth could be a sign of a more cautious insurer environment as vehicle sales stagnate and premiums continue to be under pressure.
Impact of passenger vehicle sales on insurance
CareEdge Ratings stated in a report that “the muted sales in passenger vehicles is one of the main factors contributing to the slow growth in motor insurance rates.” The insurance industry is feeling the impact of the auto industry’s struggles, especially in the passenger car segment. The demand for new insurance policies has slowed down as fewer cars are on the roads, resulting in a softer premium increase. The subdued market is increasing the pressure on motor insurance companies, reducing the growth momentum that was once more dynamic.
Premium Collections under Pressure

Emkay Research’s second-quarter insurance sector preview stated that “the sluggish increase in vehicle sales is likely to continue to have a significant impact on the total premium collection within the motor segment.” The auto market is facing persistent challenges. This has a direct impact on the premium generation, which creates headwinds for insurance companies. Slow vehicle sales act as a brake for new policy issuances and reduce growth opportunities in the motor insurance sector. The ongoing pressure on premium collection highlights the interdependence between the automotive and insurance sectors, which is highlighted by a vulnerability shared in times of slowdown.
The Challenges of Regulatory Stagnation

The motor insurance industry has also been challenged by the lack of revisions to third-party rates that are regulated and governed by the IRDAI over the last two years. Insurance companies are struggling to maintain profitability without an adjustment that reflects rising costs and claims. Lack of rate increases is pinching margins. This is especially true as claims rise. The pressure on insurers who are already struggling with slow vehicle sales and low premium growth will only increase. The industry is increasingly concerned about this regulatory stagnation.
Increased pressure on loss ratios
In FY24, the combined loss ratio of the insurance industry — calculated by adding up all incurred expenses and losses and dividing it by total premiums — was a very significant 118.5%. As claims and awards continue to rise, insurers are preparing for an increase in pressure on the combined loss ratio. Private players are taking a more conservative approach to underwriting. This is especially true in the segment of large commercial vehicles, where there remains a high level of risk. This conservative approach reflects a growing concern about profitability as the industry struggles with claims that are escalating and threaten to inflate the loss ratios for the coming fiscal years.
Need for Strategic Alignments
“Motor third-party rates have been unchanged for the past two year, putting significant pressure on general insurers, particularly those in the public sectors. This challenge is compounded by a significant decline in motor vehicle purchases. T. Babu Paul is the Executive Director of National Insurance. The ongoing stagnation of rates and the weak sales performance highlight the intersection between regulatory frameworks, market dynamics and the industry.
A Proactive Approach to Rate Adjustments

Sanjeev Mantri MD and CEO, ICICI Lombard General Insurance, stated that “we remain committed to pursuing adjustment because, at an industry level, certain segment still warrants an increase in third party rates while there may also be other segments where reductions can help rebalance our overall portfolio.” This proactive approach demonstrates the need for a nuanced motor insurance strategy that takes into account both the challenges as well as the opportunities. Insurers aim to improve their balance sheets by recalibrating the rates in various segments.
Frequently Ask Question
Question : Why do car sales decline?
Answer : The affordability issue has also manifested clearly in the entry level auto segment where smaller hatchbacks struggle to gain traction.
Question : What could cause a decrease in demand for cars?
Answer : A decline in income will have the opposite impact, shifting the demand curve leftward, towards. The average person has less money, and is therefore less likely to purchase a car for a certain price. This reduces the demand.
Question : What affects car sales the most?
Answer : Economic factors may be the most important factor in determining car sales.
Question : What factors influence the demand for cars?
Answer : There are several factors that influence the demand for automobiles:
- Public transport is an option.
- The price of the car you are going to buy.
- The price of alternatives on the market.
- The individual’s income.
- Gasoline price
- The cost of servicing and maintaining the vehicle.

